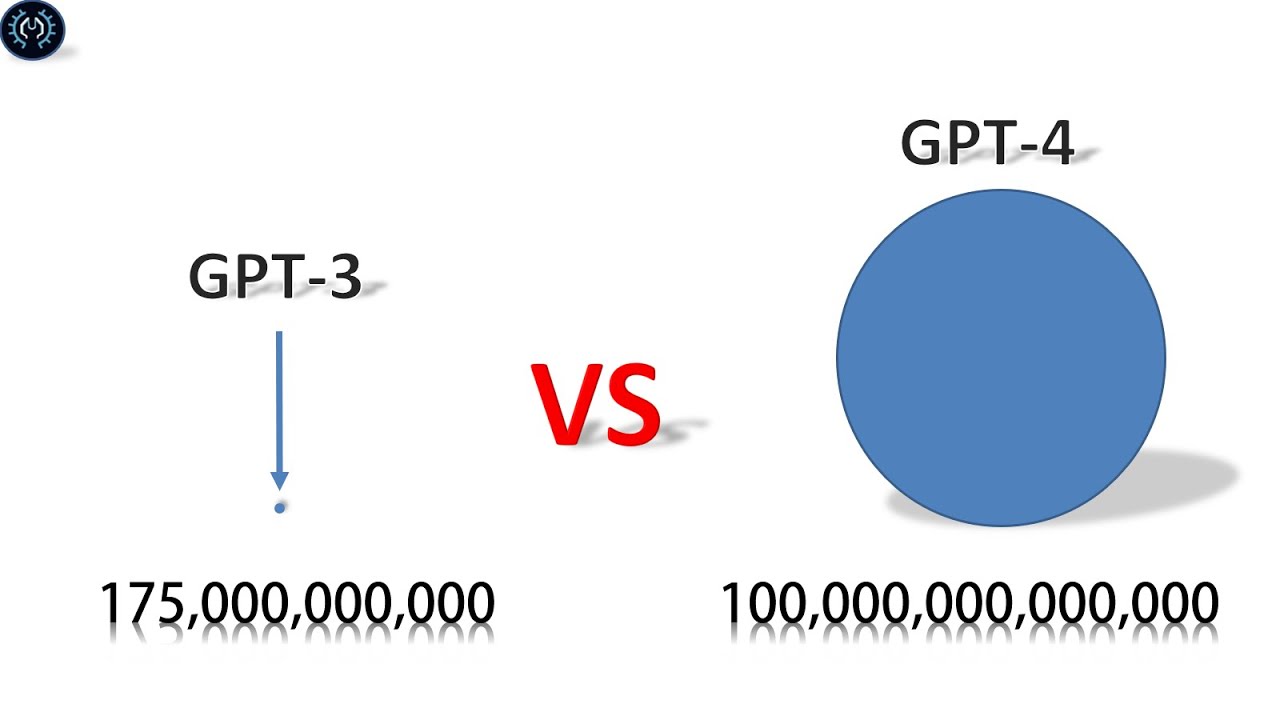
GPT-3/4
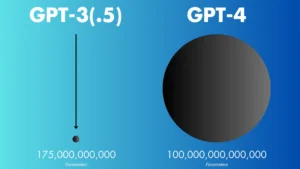
The GPT-3 and GPT-4: The Titans of AI Language Models:
Introduction:
GPT-3/4: The world of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has been dramatically shaped by advances in Natural Language Processing (NLP), with the GPT (Generative Pretrained Transformer) models standing at the forefront of this revolution. Developed by OpenAI, GPT-3 and GPT-4 are among the most sophisticated AI language models ever created. Their ability to generate human-like text, understand context, and perform complex tasks has taken AI’s capacity to new heights, transforming various industries in the process.
This article delves into the features, capabilities, and impact of GPT-3 and GPT-4, highlighting the distinctions between these two models and their transformative role in AI-driven applications.
What is GPT?
GPT models are part of a family of deep learning models known as Transformers, which have become the foundation for state-of-the-art NLP systems. The original GPT model, released in 2018, introduced the concept of using massive, unsupervised datasets to pretrain language models. These models are based on the Transformer architecture, which processes input data using self-attention mechanisms, enabling the models to understand and generate text based on contextual relationships between words.
Unlike traditional language models that only consider a limited window of text, GPT models can process longer stretches of text, allowing them to produce more coherent and contextually relevant output. Each successive version—GPT-2, GPT-3, and GPT-4—has grown significantly in both size and capability, with GPT-4 being the latest and most advanced iteration.
GPT-3: A Leap in Language Understanding:
GPT-3, released in June 2020, was a breakthrough in the AI community due to its enormous size and the sheer versatility of its applications. It consists of 175 billion parameters, making it by far the largest language model at the time of its release. These parameters are the internal weights that GPT-3 learns during its training process, allowing it to understand the complex relationships between words, phrases, and sentences.
Key Capabilities of GPT-3:
- Natural Language Understanding and Generation:
GPT-3 is renowned for its ability to generate human-like text. It can respond to questions, engage in dialogue, summarize information, and even write creative content such as poems or stories. What sets GPT-3 apart from earlier models is its ability to handle open-ended tasks without needing task-specific fine-tuning. Users can input a prompt, and GPT-3 will generate responses that are not only relevant but also contextually aware. - Few-Shot Learning:
One of GPT-3’s most impressive features is its proficiency in few-shot learning. Unlike traditional models that require large datasets for training on specific tasks, GPT-3 can perform tasks with minimal examples. For instance, when asked to translate text, solve math problems, or classify data, GPT-3 can often perform well even after seeing just a few examples of the task. - Wide Range of Applications:
GPT-3’s versatility spans a multitude of applications:- Text completion: GPT-3 can take a partial sentence or paragraph and complete it in a coherent manner.
- Chatbots: It powers conversational agents that can engage with users on various topics.
- Creative writing: GPT-3 can generate content such as short stories, poems, or scripts.
- Coding assistance: It can generate code snippets and help with programming challenges in various languages.
- Data analysis: It can summarize data, generate reports, and even answer questions based on a dataset.
Limitations of GPT-3:
Despite its groundbreaking capabilities, GPT-3 has certain limitations:
- Lack of Common Sense and Reasoning: GPT-3 can sometimes produce text that appears logical on the surface but lacks common sense. It may generate plausible-sounding but incorrect information, as it is primarily focused on pattern matching rather than true understanding.
- Bias in Output: Like other large models, GPT-3 inherits biases from the vast amounts of internet data it was trained on. This can lead to biased or problematic outputs in certain contexts.
- Memory Limitations: GPT-3 doesn’t have long-term memory across sessions. Each prompt is processed independently, meaning it cannot “remember” previous interactions unless those are explicitly fed into the model again.
GPT-4: A More Advanced, Contextual AI:
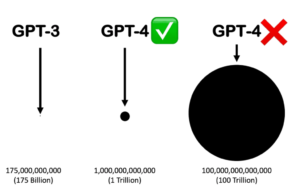
GPT-4, released in March 2023, builds on the strengths of GPT-3 while addressing many of its limitations. Although OpenAI has not publicly disclosed the exact number of parameters in GPT-4, it is widely assumed that GPT-4 is even larger than its predecessor, offering greater accuracy, depth, and flexibility in its responses.
Key Innovations in GPT-4:
- Improved Contextual Understanding:
GPT-4 features an enhanced ability to maintain context over longer conversations or documents. While GPT-3 could handle context for several paragraphs, GPT-4 can process significantly more tokens (units of language), meaning it can analyze and generate text across longer documents or more extended conversations with greater coherence. This allows GPT-4 to excel in tasks such as legal document analysis, technical writing, and academic research. - Better Handling of Ambiguity and Nuance:
GPT-4 demonstrates a better grasp of ambiguous or nuanced language. It can interpret sentences with multiple meanings more effectively, choosing the most appropriate interpretation based on the context. This makes it more suitable for complex tasks like contract drafting, medical diagnosis, and philosophical discussions, where subtleties in language are critical. - Factual Accuracy and Reasoning:
One of the key improvements in GPT-4 is its enhanced ability to provide accurate, factual information. OpenAI has made strides in reducing the model’s tendency to “hallucinate” (generate incorrect or nonsensical information). Additionally, GPT-4 exhibits better reasoning abilities, improving performance in tasks that require logical deduction, such as solving math problems or complex riddles. - Multimodal Capabilities (GPT-4 Vision)
GPT-4 introduced multimodal capabilities, meaning it can process both text and images. This represents a major advancement, as GPT-4 can now generate descriptions of images, analyze visual data, and respond to image-based prompts. For example, users can upload an image and ask GPT-4 to describe it or answer questions about its contents. This opens the door to a wide range of applications, from image-based search engines to AI-driven content creation using both visual and textual elements.
Applications of GPT-4:
- Healthcare and Diagnostics:
GPT-4’s improved reasoning and contextual abilities make it ideal for applications in healthcare. It can analyze medical data, provide potential diagnoses, and assist with research. By processing both text and image data (such as medical images), GPT-4 offers the potential to assist in complex fields like radiology or pathology. - Legal and Compliance:
In the legal field, GPT-4 is proving useful for analyzing complex legal documents, drafting contracts, and ensuring compliance with regulations. Its ability to understand nuanced language and maintain context over longer documents helps automate many tasks traditionally handled by human lawyers. - Content Creation and Media:
Content creators are leveraging GPT-4 to generate highly tailored, coherent, and creative content for marketing, journalism, and entertainment. Whether producing long-form articles, video scripts, or interactive stories, GPT-4’s contextual understanding and creative flexibility make it a powerful tool for media professionals. - Language Translation:
GPT-4 provides even more accurate translations than GPT-3, with a deeper understanding of idiomatic expressions, cultural nuances, and slang. This is vital for applications in global communication, business, and diplomacy.
GPT-3 vs GPT-4: Key Differences:
- Size and Complexity: While the exact size of GPT-4 has not been confirmed, it is generally believed to be larger and more complex than GPT-3, allowing it to generate more accurate and nuanced responses.
- Contextual Capacity: GPT-4 has a significantly larger context window, meaning it can process and generate text based on a much larger volume of input, making it more effective for long-form content and extended conversations.
- Factual Accuracy: GPT-4 has made significant strides in reducing hallucinations and providing more factually accurate responses compared to GPT-3, making it more reliable for tasks requiring precision.
- Multimodal Capabilities: GPT-4’s ability to process both text and images is a major advancement over GPT-3, which is limited to text-based input and output.
The Future of GPT Models:
GPT-3 and GPT-4 represent monumental advancements in AI and NLP, but the future holds even more promise. As models grow in complexity and are better able to understand context, reason, and interact with multiple forms of data (text, images, audio, and more), we can expect AI to become even more deeply integrated into our daily lives.
GPT-5 and Beyond: Future versions are likely to bring even more improvements in multimodal processing, factual accuracy, ethical guardrails, and computational efficiency. We may see AI models that can process video, interpret emotions, or even simulate real-time interactions in virtual environments.
Conclusion:
GPT-3 and GPT-4 have transformed the landscape of AI and NLP, with their unprecedented ability to generate human-like text, perform complex reasoning, and understand context. While GPT-3 brought a new level of versatility and scale to AI models, GPT-4 expanded on this with improvements in accuracy, multimodal capabilities, and reasoning.
Download Here